Thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disease is a disorder of the cardiovascular system, characterized by inflammation of the veins accompanied by blood clots. This condition causes sore, pain, fever, etc. and is also dangerous because if the blood clots migrate into the body, this may cause fatal complications. It is encountered more frequently in the legs, and in women after the age of 50 years.
Thrombophlebitis involves total or partial obstruction of the venous wall by intravenous coagulation, or inflammation of the venous wall and blood clots that may obstruct all or part of the vein, making difficult blood circulation. First, the process is triggered, usually in leg and foot veins extending from the main veins of the calf and then the femoral vein and iliac. Basically, it starts the formation of a platelet agglutination, which forms white clot, which shall be deposited in the fibrin and red blood cells to complete sealing of the vein, followed by massive blood clotting, forming red clot. At first, the clot is adherent venous wall, so more blood will pass and embolism is possible. Later, the clot is adherent implying thrombophlebitis.
The first symptoms of thrombophlebitis: superficial vein inflammation, temperature, increased pulse, increased tension in the calf or cyanosis, anxiety, fear, hyperthermia, skin, pain in the dorsal region live to palpation of the calf, edema. When the disease has advanced, there is massive swelling, which extends to the groin. Signs of thrombophlebitis are discrete: continuous pain in walking, difficulty walking and limping, anxiety and tachycardia, the emergence of a tough cord, red and sensitive in the affected area, usually in the veins.
Evolution of thrombophlebitis is prolonged over months or years after healing venous circulation disorders persisted. In the first week there is a great danger of pulmonary embolism.
One reason for the occurrence of thrombophlebitis is heart failure and prolonged immobilization and leukemia, anemia, typhoid fever, cancer, abscesses and necrotizing pneumonia, trauma, varicose veins, treatment with antibiotics and steroids, pregnancy and confinement, varicose veins (“thrombi” can form in superficial veins dilated, causing superficial thrombophlebitis), physical trauma to the veins, obesity, smoking, liver and spleen disorders, endocrine disorders.
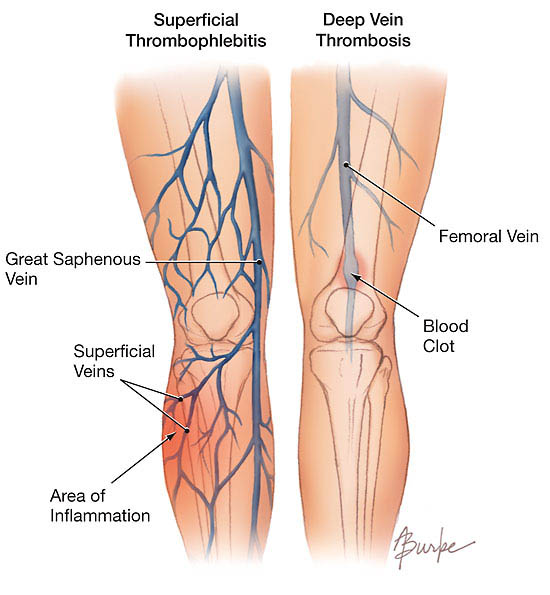
Depending on the affected veins, this may be superficial or deep thrombophlebitis. In the case of superficial venous thrombosis of subcutaneous, veins are affected, and thrombophlebitis deep muscle veins are obstructed.
Prophylaxis is the treatment of thrombophlebitis circulatory stasis (varicose veins) and administration of anticoagulants in patients prone: obesity, cardiac embolism prophylaxis.
Thrombophlebitis complications are migratory and recurrent, varicose thrombophlebitis, thrombophlebitis with arterial spasm (blue phlebitis, accompanied by gangrene). Also, filling the muscle veins, called deep thrombophlebitis, is a major risk since thrombi may detach from the vein wall and cause pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction or cerebral vascular attack.
Superficial thrombophlebitis is not an immediate danger to the patient, but in particular situations blocked veins can lead to infections or damage to adjacent tissue because of poor peripheral circulation.
Some treatment from alternative medicine consists in acupuncture and phytotherapy and medication involving reduced blood pressure, restoring balance in liver and spleen and regulation of endocrine imbalances.