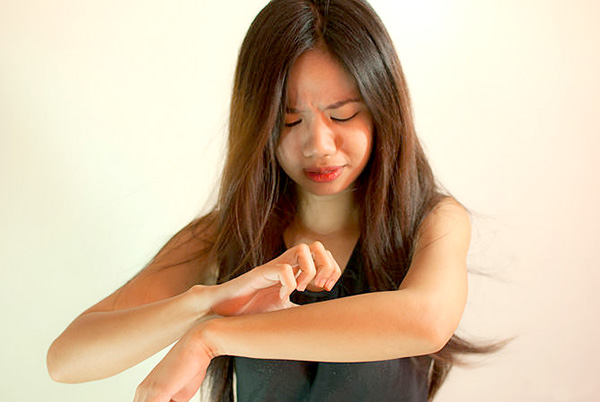
Once, scabies was a shameful disease affecting especially those with poor hygiene and living conditions. However, today we know that scabies can affect anyone, regardless of social status or possibilities.
What is scabies?
Scabies is a skin disease, a contagious dermatitis, caused by Scabies Sarcoptes Varietas Hominis, affecting mostly certain areas of the body. It can occur at any age and affects men and women equally; most affected are children and the elderly people.
Causes of scabies:
The disease is caused by a parasite which has four pairs of legs and a cerebrospinal thorax, with a round body. Females are larger than males and are found in the parasitic stratum corneum of the epidermis, forming true tunnels under the skin where they lay eggs every day. Larvae will resurface the skin turning initially in nymphs, and after this relatively small period they grow adults and then will subsequently multiply. After this cycle that lasts two weeks, the males die, and the females are parasitising the skin again.
Transmission is usually through physical contact (and sexually) with a contaminated person, using the same clothing, bedding or the same personal or household items. The mites can survive for four days without a human host.
Parasites choose the host body, namely the skin: elbows, knees, wrists, fingers, breasts, armpits, navel and the groin area.
The incubation period is 2 weeks but may extend up to 6 weeks for the contagious affected person.
Risk factors:
– Congestion;
– Tourism;
– Promiscuity;
– Use of the same clothing or linens by the same persons;
– Immunodeficiency;
– Nosocomial infection;
– Atopic eczema;
– Poor socioeconomic status;
– Sexual libertinism.
Symptoms of scabies:
The first symptom is pruritus (itching) and allergic reaction due from scabies mites. Itching is exacerbated especially at night, or after a bath. The skin becomes irritated, itchy and sensitive.
The rash has a symmetrical distribution with the following location:
– Interdigital spaces (between the toes);
– Ribs;
– The front of the armpit;
– Hands;
– The area around the nipples;
– The area around the navel (belly button);
– Belt area;
– Scrotum;
– Santa buttock;
– Knee;
– External edges of the feet.
Continue to the next page to read the full article: