If a doctor consultation is delayed, because of massive destruction of beta cells, absolute deficit of insulin causes marked hyperglycemia; body uses protein and fat burning for energy production. Ketone bodies and fatty acids appear in excess and install one of the most severe complications of type 1 diabetes (DKA) – requiring emergency intervention.
In some cases, it is observed that for a short period of time, weeks or months, the pancreas can secrete insulin. This period is called the “honeymoon” and insulin is not required, or, only a small amount of insulin is administered, depending on the secretory capacity of the pancreas. After the “honeymoon”, administration of insulin is mandatory.
Those with type 1 diabetes will follow an individualized treatment comprising of:
- – Administration of insulin;
- – Proper diet;
- – Exercise program;
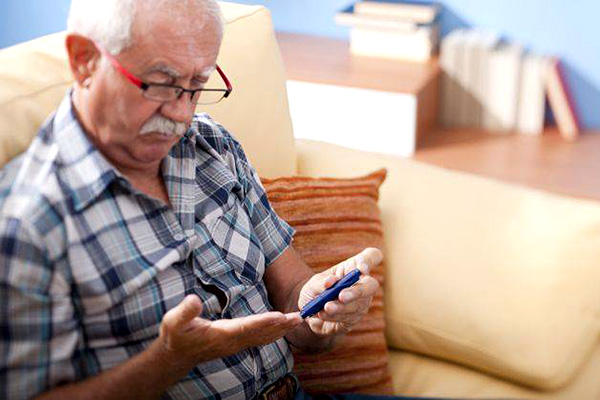
- – Daily monitoring of blood glucose;
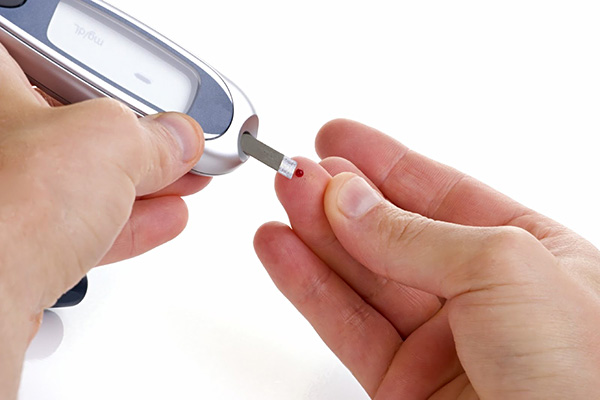
Blood sugar levels of people with insulin-dependent diabetes are often outside normal limits, due to insulin injection that may cause rapid (only for a few minutes) drop in blood sugar (hypoglycemia), which is a medical emergency. On the other hand, hyperglycemia is developed slowly over hours or days. If hyperglycemia persists, DKA occurs.
Over time, tissue and organ injuries occur due to persistent hyperglycemia which is producing diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic neuropathy, heart disease (myocardial infarction) and vascular (stroke and vascular obstruction, especially in the legs). If the blood sugar is kept within safe limits, the appearance of such serious complications can be prevented. Although, some patients develop complications even with good control of blood sugar.
Increased patient compliance (patient cooperation with specialist and religiously follow the prescribed treatment) determines a sense of security for the patient, feeling that his disease is under controls – and this gives a good feeling.
Risk factors:
Risk factors for type 1 diabetes are:
– Family history of type 1 diabetes increases the risk of islet cell antibodies, but not the risk of the person making type 1 diabetes. Only 10-15 % of patients with type 1 diabetes had this disease in family history:
– The risk is 6% if the father has insulin-dependent diabetes;
– Where brothers / sisters have type 1 diabetes the risk of disease is 5%;
– If the mother has type 1 diabetes, the risk to make diabetes is 2%;
– In the case of identical twins, the risk is 30-50%;
– If a parent and a brother / sister have / had insulin-dependent diabetes, the risks are 30%;
– People with white skin are at increased risk for type 1 diabetes compared with African-Americans, Hispanics and Asians;
– The presence of antibodies – anti beta cells in the blood – both in familiar history and the presence of anti-beta cells, predisposing to the development of type 1 diabetes;
– Viral infections during childhood – Enterovirus infection, especially Coxsackie b infection increases six times the risk of type 1 diabetes. However, a child who had a Coxsackie b infection will not necessarily develop the disease;
– Consumption of cow milk – infants fed with cow’s milk before the age of 4 months were at significantly higher risk of diabetes mellitus type 1, if associated with a genetic predisposition or the presence of other factors risk;
Children who have siblings with diabetes and who drank more than 236.6 ml of milk per day shows a four-time’s higher risk of having anti-beta cells and developing insulin-dependent diabetes. Experts do not know the role of cow’s milk in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes.
Medical emergencies:
– A person who loses consciousness and its breathing seems like a green apple odor (acetone) – diabetic ketoacidosis.
Specialist consultations:
– Presence of symptoms of intense thirst, excessive urination, weight loss, increased appetite – all these require medical attention for laboratory investigations;
– Person who has a family history of insulin-dependent diabetes and wants to test for diabetes;
Recommend specialists:
- – Endocrinologist;
- – General practitioner (GP);
- – Family doctor (GP);
- – Internist;
- – Pediatrician;
Medical treatment:
Continue to the next page to read the full article: