There are many healthy habits that children can adopt to lead happy and fulfilling lives. Some of the most important healthy habits for children include eating a nutritious diet, being physically active, getting enough sleep, and maintaining good hygiene.
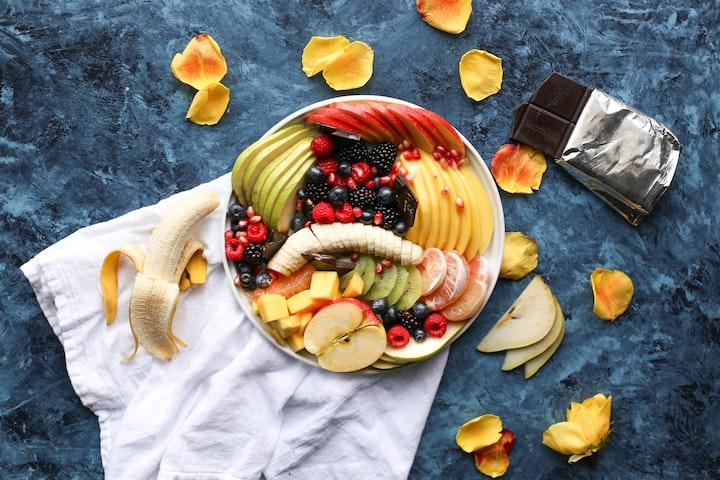
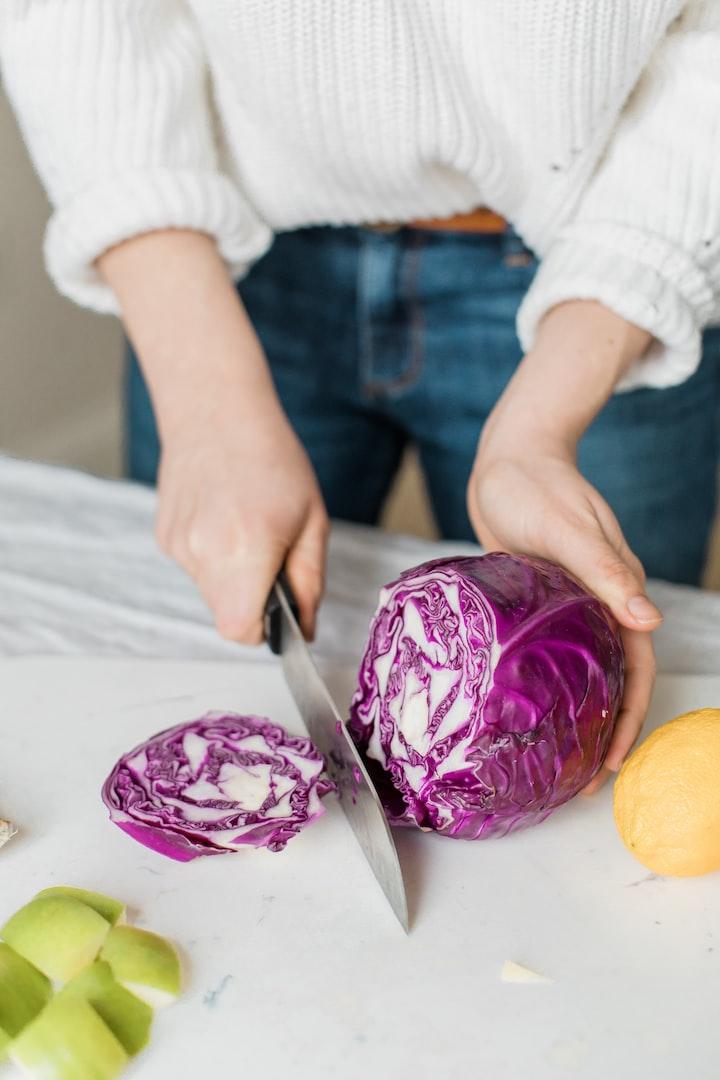
A nutritious diet is vital for children to grow and develop properly. They should eat a variety of foods from all the food groups, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy. It’s also important for kids to limit sugary drinks and snacks.
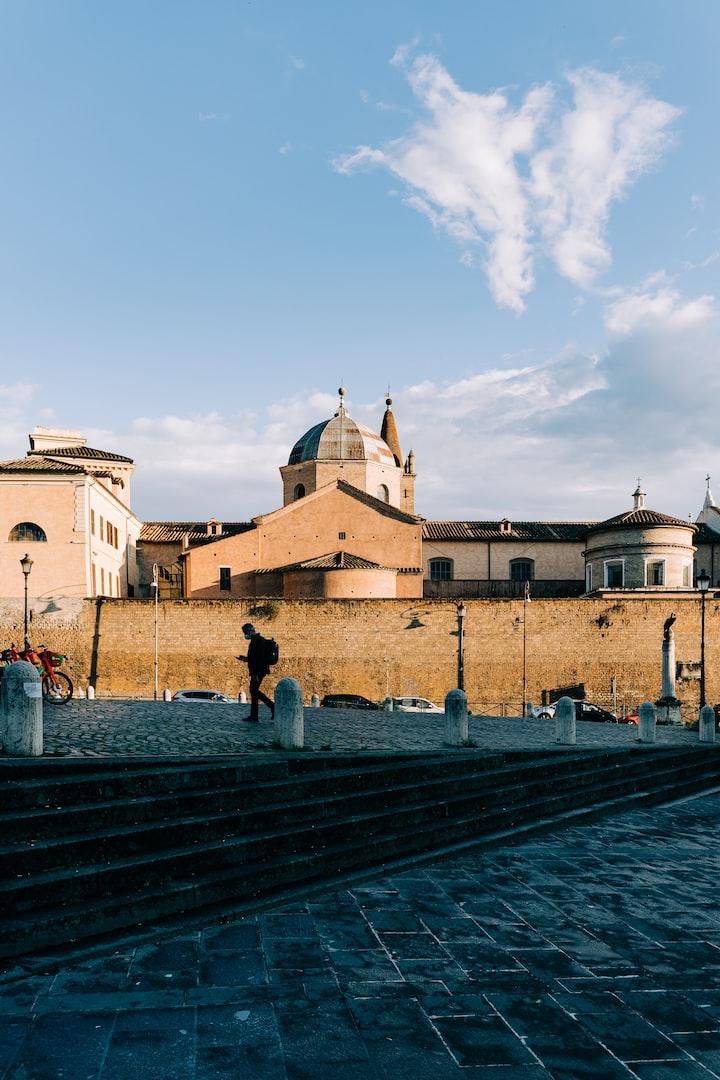
Physical activity is another key healthy habit for kids. Children should get at least 60 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity every day. This can include playing sports, riding bikes, running around at the park, or dancing.
Getting enough sleep is essential for children’s overall health and well-being. Most school-aged children need between 9 and 12 hours of sleep each night in order to function properly during the day. Good sleeping habits can be established by having a regular bedtime routine and avoiding caffeine before bedtime.
Read More »We Listed the Healthy Habits of Children